data structure and algorithm
我希望每个人对算法和数据结构是什么有一个深刻的认识,所以我们会在每一篇的文章的开始给你灌输下面的这些知识点:
1、数据结构是一门研究组织数据方式的学科,有了编程语言也就有了数据结构,学好数据结构可以让你写出更漂亮更高效的代码(时间复杂度和空间复杂度);
2、算法其实就是解决我们生活中遇到的问题的计算方法;
3、程序=数据结构+算法;要学好数据结构和算法就要在日常生活中把遇到的问题尝试用程序去解决
4、数据结构是实现一个算法的基础,所以想要学好算法,需要把数据结构学到位;
5、数据结构分为线性结构和非线性结构;线性结构的特点是数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系;
6、线性结构又有顺序存储结构和链式存储结构两种的存储结构,顺序存储结构中存储元素是连续的,而链式存储结构中存储元素不一定是连续的;
顺序表
顺序存储结构对应的数据结构就是数组,所以以数组作为底层数据结构的顺序表的特点是由数组的特点决定的;
数组
数组这种数据结构的特点是能按下标索引快速寻找到所要查找的元素,但如果需要在头部或者中间添加或者删除元素,需要移动添加或删除位置后面所有的元素,所以以数组作为底层数据结构的顺序表是一种改查效率高而增删效率低的数据结构;
同时数组还有另外一个性质就是在创建数组时需要提前知道数组的大小,但在实际开发中我们并不能提前知道我们容器所要盛放元素的个数,这个时候当我们所需要盛放的元素个数超过数组的大小时就需要动态的增加数组的大小,而动态增加数组大小的过程是创建一个更大的数组,然后把原数组中的元素添加到新建的数组中并返回新建的数组;这个过程其实是非常低效的,所以每次应该扩容多大也是需要有一个良好的策略的,我们将会在后面对jdk提供的ArrayList顺序表的底层扩容策略进行详细讲解;
数组分为一维数组和多维数组,我们常说的数组就是一维数组,一维数组是线性结构的而多维数组是非线性结构的;
一维数组的创建:
int[] ins=new int[n];
int ins[]=new int[n];
二维数组的创建:
int[][] ins=new int[x][y];
稀疏数组
在某些特定的应用中,我们会发现这样的一个需求,我们需要保存一个数组到磁盘中并在之后从磁盘中恢复这个数组,但因为数组中元素的默认值为0,0在我们对数组的应用中为无意义数值,所以我们在存储的时候一般只需要存储有意义的数组即可,这个时候我们就需要将数组转化为稀疏数组再进行存储工作;
将数组转化为稀疏数组:
public class ArrayToSparseUtil {
static int[][] sparseArrays=null;
public static void transfer(int[][] arrays,String path) throws IOException {
int rowLen=arrays.length;
int columLen=arrays[0].length;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<rowLen;i++){
for(int j=0;j<columLen;j++){
if(arrays[i][j]!=0){
sum++;
}
}
}
sparseArrays=new int[sum+1][3];
sparseArrays[0][0]=rowLen;
sparseArrays[0][1]=columLen;
sparseArrays[0][2]=sum;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<rowLen;i++){
for(int j=0;j<columLen;j++){
if(arrays[i][j]!=0){
count++;
sparseArrays[count][0]=i;
sparseArrays[count][1]=j;
sparseArrays[count][2]=arrays[i][j];
}
}
}
File file=new File(path);
FileWriter fw= null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(file);
for (int[] rows:sparseArrays
) {
for (int num:rows
) {
fw.write(num+"\t");
}
fw.write("\r\n");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
fw.close();
}
}
public static void printArrays(){
for (int[] rows:sparseArrays
) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\r\n",rows[0],rows[1],rows[2]);
}
}
}
将稀疏数组转化为原来的数组:
public class SparseToArrayUtil {
public static int[][] transfer(String path) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String line;
int row=0;
int[][] sparseArray = null;
int rowLen=0;
int columLen=0;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
String[] strs=line.split("\t");
if(row==0){
rowLen=Integer.parseInt(strs[0]);
columLen=Integer.parseInt(strs[1]);
int sum=Integer.parseInt(strs[2]);
sparseArray=new int[sum+1][3];
}
for(int i=0;i<strs.length;i++){
sparseArray[row][i]=Integer.parseInt(strs[i]);
}
row++;
}
int array[][]=new int[rowLen][columLen];
for(int i=1;i<sparseArray.length;i++){
array[sparseArray[i][0]][sparseArray[i][1]]=sparseArray[i][2];
}
return array;
}
}
测试类:
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int array[][]=new int[11][11];
array[0][1]=1;
array[1][2]=2;
ArrayToSparseUtil.transfer(array,"D:\\a.txt");
System.out.println("稀疏数组为:");
ArrayToSparseUtil.printArrays();
int[][] arrays=SparseToArrayUtil.transfer("D:\\a.txt");
System.out.println("原数组为:");
for (int[] ins:arrays
) {
for (int ii:ins
) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",ii);
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
测试结果:
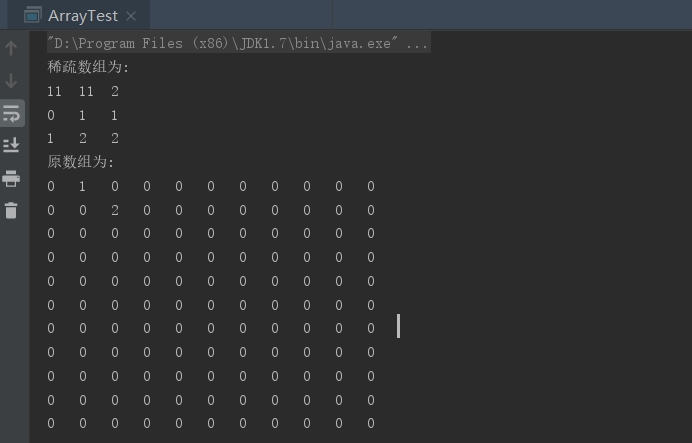
ArrayList
源码解析:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA will be expanded to
* DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
private transient Object[] elementData;
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
super();
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
通过对这部分源代码的解读,我们可以知道当我们实例化一个ArrayList的过程中,它会在内部创建一个数组,而数组的大小可以是由参数指定,也可以是由传入的集合对象的大小觉得,或者是默认的大小;
/**
* Increases the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if real element table
? 0
// larger than default for empty table. It's already supposed to be
// at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
通过对这段源码的阅读,我们可以探究出ArrayList底层的扩容机制,我们可以知道当集合的容量大小小于最小保障容量大小时,会调用grow方法进行扩容;通过对grow方法的分析,int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity » 1)的作用是在原有容量的基础上扩容50%,即扩容后的容量为原容量的1.5倍;
